This photo captures what the breast expanders look like. They're hard and sit very high.
A common breast reconstruction technique is tissue expansion, which involves expansion of the breast skin and muscle using a temporary tissue expander. A few months later, the expander is removed and the patient receives either microvascular flap reconstruction, or the insertion of a permanent breast implant. This type of breast reconstruction requires two separate operations.
During implant reconstruction, if you're having the implant inserted at the same time as mastectomy (immediate reconstruction) and enough tissue is available to cover the implant, your plastic surgeon will place the breast implant under your chest muscle after your breast surgeon has removed the breast tissue.
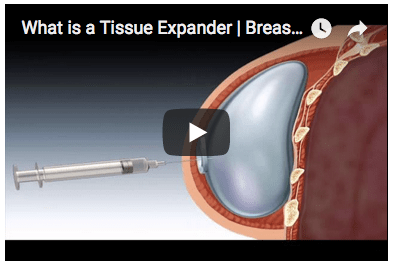
If a large amount of skin is removed during mastectomy or you're having the staged approach to implant reconstruction (delayed-immediate reconstruction), your plastic surgeon places a tissue expander between the skin and chest muscle after your breast surgeon has removed the breast tissue. A tissue expander is an implant that’s more like a balloon. It stretches the skin to make room for the final implant.


The expander has a port (a metal or plastic plug, valve, or coil) that allows the surgeon to add increasing amounts of liquid (a salt water solution) over time (between 2 to 6 months) until the skin gradually is stretched enough to accommodate the implant.


If you have an expander put in and there is any chance you will have radiation therapy, be sure your surgeon uses an expander with a plastic port, not a metal one.
A metal port interacts with the radiation right around the metal and produces excessive, unnecessary skin damage. If you already have an expander with a metal port, ask the plastic surgeon about possibilities that include:
- replacing the expander with an implant before starting radiation therapy
- quickly finishing expansion so an implant can be inserted before starting radiation therapy
- inserting a permanent expander (with a plastic port) that will become your implant after radiation therapy is finished
In some cases, your plastic surgeon may recommend using a surgical mesh or dermal matrix product that covers the implant and provides a structure for your skin to grow in and around. This may allow more liquid to be added to the expander during surgery, which may lower the number of times more liquid has to be added later.
Dermal matrix products are skin substitutes made from human, calf, or pig skin that has been processed and sterilized to remove all cells, which reduces the risk of disease and of your body rejecting it. What's left is a mesh-like framework of mostly collagen, a strong protein found in skin, bones, and other tissue. Human skin used for dermal matrix products is donated by tissue banks that follow American Association of Tissue Banks Standards. All skin used to make dermal matrix products is tested according to U.S. Food and Drug Administration and appropriate state regulations. There are more than ten dermal matrix products used in breast reconstruction.
AlloDerm, Strattice, NeoForm, and DermaMatrix are all dermal matrix products. These products have been used in breast reconstruction since about 1998 and are being used more frequently today, both for immediate implant reconstruction and staged reconstruction. While dermal matrix products present a possible increase in the risk of infection, there’s also a possible benefit -- reduction in scar tissue forming around the implant. Research is looking at implant reconstruction with a tissue expander using a dermal matrix product to cover the implant compared to using skin and muscle to cover the implant. The dermal matrix essentially forms a “sling” that helps form a pocket and support the lower portion of the implant, holding it in position.
Mastectomy surgery can take 2 to 3 hours to complete. If you're having an implant or tissue expander inserted at the same time, this will take about another hour or so.
If you're having implant surgery some time after mastectomy and other treatments (delayed reconstruction), surgery to insert the tissue expander may be done about 4 to 6 months after your last treatment. If many months or years have passed since your mastectomy, it still may be possible to have tissue expansion and implant reconstruction. It really depends upon the condition of the skin at the surgery site (for example, how much skin is left and how much scarring there is).
To stretch the skin, over the course of a few months you will receive a series of saline injections into the tissue expander. After each injection, you might feel some pain or pressure for a few hours. This usually goes away by the next day.
Once the skin stretching is completed, you'll most likely have more surgery to replace the tissue expander with a permanent implant. Surgery is usually scheduled about 4 to 6 weeks after the last amount of liquid has been added to the expander. Surgery to insert the permanent implant takes about an hour.
If radiation therapy is part of your treatment plan, most surgeons prefer that the radiation happen while you still have the tissue expander. This approach offers a better cosmetic result because it offers an opportunity to remove any radiation scar tissue before placing the final implant. If you’re not sure which option is right for you, it’s a good idea to seek a second opinion with another plastic surgeon who specializes in breast reconstruction. In many cases, radiated skin isn’t the best environment for an implant, so talk to your surgeon to find out his or her experience with this.
After implant reconstruction surgery: Your doctor will give you specific instructions to follow for your recovery. For detailed information on the special exercises you should do to prevent stiffness and scar tissue build-up after immediate or delayed-immediate reconstruction, as well as how to care for the dressings, stitches, staples, and surgical drains, visit the Mastectomy: What to Expect page.
It can take about 6 weeks to recover from implant surgery done at the same time as mastectomy. It's important to take the time you need to heal. It's also important to continue doing your arm exercises each day and follow any other routines your doctor or physical therapist prescribes for you.
When you have surgery to swap the tissue expander for a permanent implant (the second step of delayed-immediate or delayed reconstruction), it's usually done as an outpatient procedure, which means you don't stay overnight in the hospital. You'll still be given general anesthesia, so you'll need to have someone come with you to the hospital or clinic to drive you home. This surgery takes about an hour. Because this surgery is less involved than the mastectomy-tissue expander/implant surgery, recovery usually takes about 2 weeks (breastcancer.org).

Me feeling confident with my breast expanders, although they do feel like having cages in your chest, are very hard, and look very fake.